GPUs are crucial parts of today’s computers. They do everything from making games look great to helping with artificial intelligence and mining cryptocurrencies.
But here’s the thing: GPUs get hot when they work hard. And if they get too hot, it can hurt their performance and lifespan.
In this guide, we’ll talk about why managing GPU temperature is important.
The Impact of High Temperatures
Running your GPU at high temperatures can take a toll. It messes with performance and longevity. When things heat up too much, the GPU might kick in its thermal throttling mode – a safety feature that dials down performance to cool things off.
But that means slower frame rates, annoying stutters, and even crashes, especially when you’re deep into graphics-heavy stuff like gaming or video editing.
And here’s the kicker: if your card keeps getting roasted, its components start to suffer. That’s like a slow burn on its lifespan, and the risk of it giving up altogether goes up.
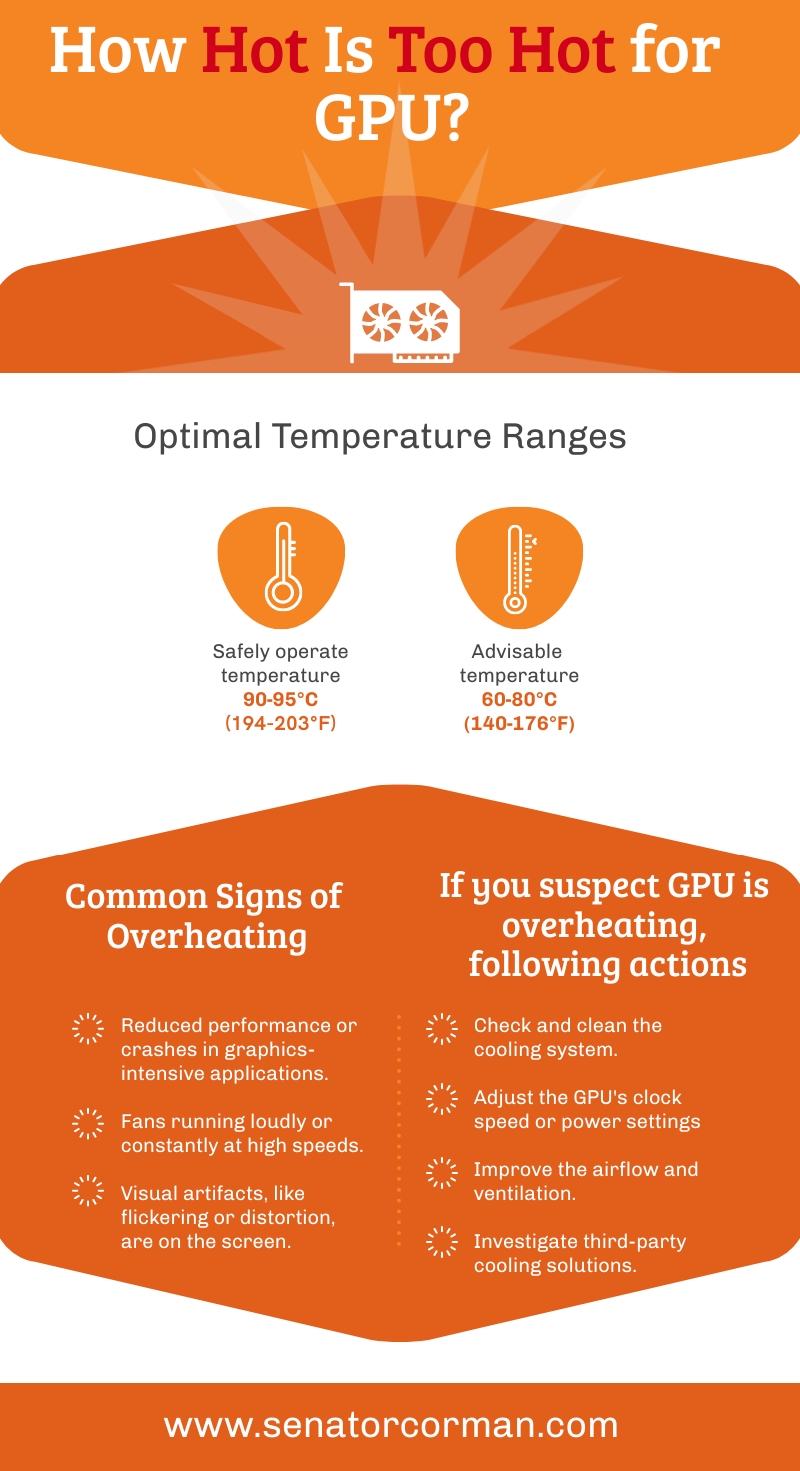
Optimal Temperature Ranges
While optimal temperature ranges may vary depending on the specific GPU model and manufacturer, most of them are designed to operate safely at temperatures up to 90-95°C (194-203°F).
However, it is advisable to keep temperatures well below this limit, ideally in the 60-80°C (140-176°F) range.
High-performance Graphics Processing Units, like those used in gaming rigs and workstations, tend to have higher temperature tolerances, while low-power ones found in ultrabooks and tablets may require lower operating temperatures to prevent overheating.
Factors Affecting Temperature
Temperature can be affected by various factors. Overclocking, which boosts a GPU’s clock speed for better performance, increases heat production.
However, this can lead to overheating and instability. Inadequate cooling, such as passive heat sinks or struggling fans and liquid coolers, can also raise temperatures.
Common Signs of Overheating

Overheating GPUs can manifest in several ways, including:
- Reduced performance or crashes in graphics-intensive applications.
- Fans running loudly or constantly at high speeds.
- Visual artifacts, like flickering or distortion, are on the screen.
If you suspect that your GPU is overheating, consider taking the following actions:
- Check and clean the cooling system to ensure it’s functioning properly.
- Adjust the GPU’s clock speed or power settings to reduce heat generation.
- Improve the airflow and ventilation in your computer case.
- Investigate third-party cooling solutions, like aftermarket heat sinks or liquid cooling systems.
Tips for Maintaining

Here are some tips to consider:
- Ensure proper ventilation: Good airflow is crucial for heat dissipation. Make sure your computer case has adequate intake and exhaust fans, and keep the area around the computer free of clutter and dust.
- Regular cleaning: Dust accumulation can reduce the effectiveness of heat sinks and fans. Clean your computer’s interior and cooling system regularly, using compressed air to remove dust.
- Avoid overclocking: While it can improve performance, overclocking can also increase heat generation. If you’re concerned about temperature, consider running your GPU at stock settings.
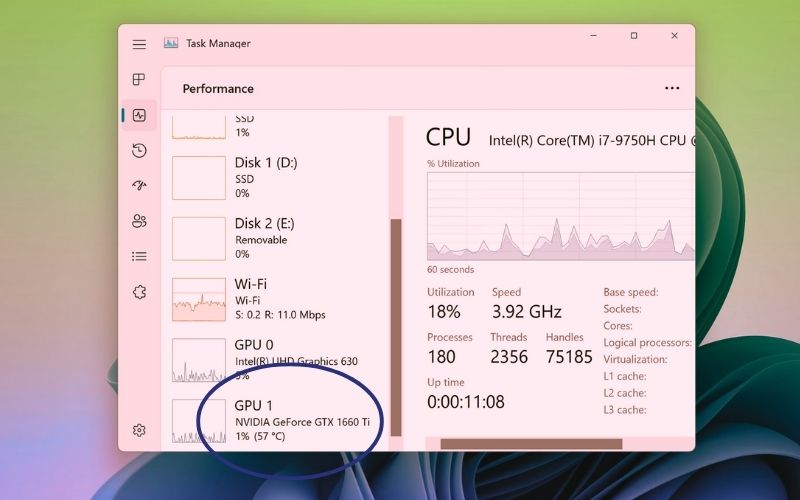
- Monitor GPU temperature: Use software like HWMonitor, MSI Afterburner, or GPU-Z to monitor your GPU’s temperature and adjust settings if necessary.
Cooling Methods
Air Cooling is one of the most common methods. It involves using fans to circulate air over the graphics card, effectively removing heat from the heatsink. While air cooling is simple and effective, it may not be sufficient for high-end GPUs or when used in hot environments.
Liquid Cooling, another popular option, utilizes a liquid (such as water or coolant) to absorb heat from the GPU. This heat is then transferred to a radiator for dissipation. Liquid cooling is highly efficient and allows for greater overclocking potential, but it is also more complex and expensive compared to air cooling.
Phase-change cooling is a specialized method that employs a refrigerant to rapidly cool the GPU to extremely low temperatures. While highly effective, it requires specific equipment and comes with a higher cost.
Passive Cooling relies on a heatsink without any fans. It is a quiet and straightforward approach, but similar to air cooling, it may not meet the demands of high-end GPUs or hot conditions.
How to Monitor and Detect Issues?
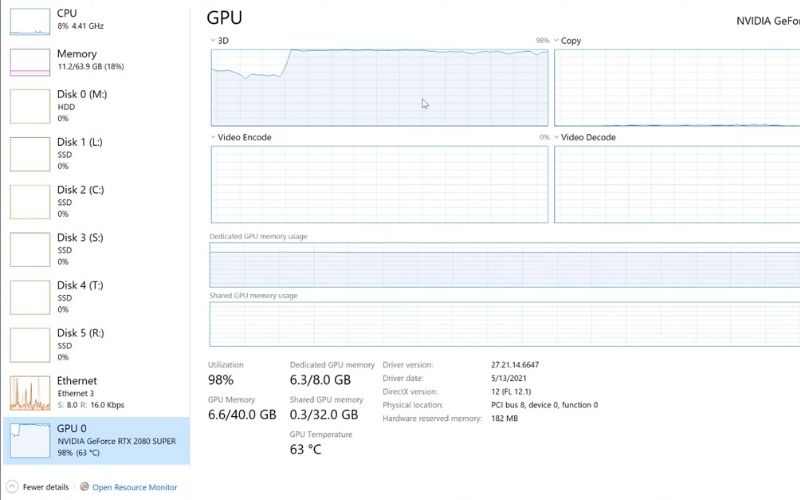
Several software applications can help you keep an eye on GPU temperatures, including:
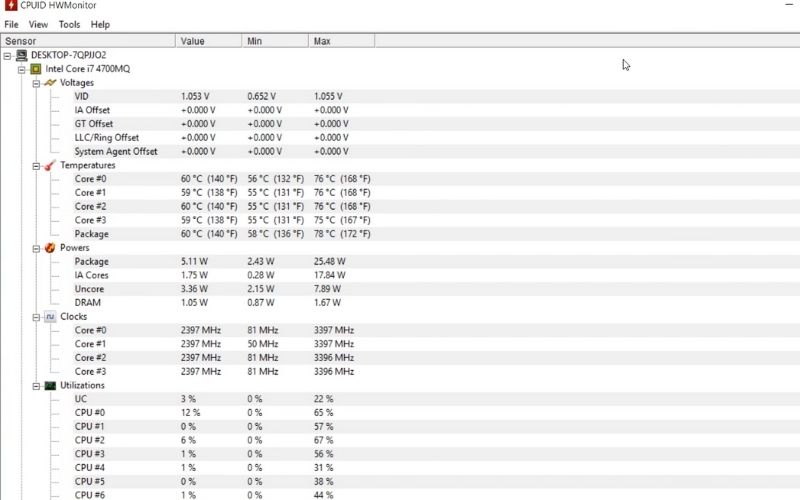
- HWMonitor: A comprehensive hardware monitoring tool that displays various system parameters, including Graphics Processing Units’ temperature.
- MSI Afterburner: A popular overclocking utility that also provides real-time monitoring of GPU temperature, usage, and fan speed.
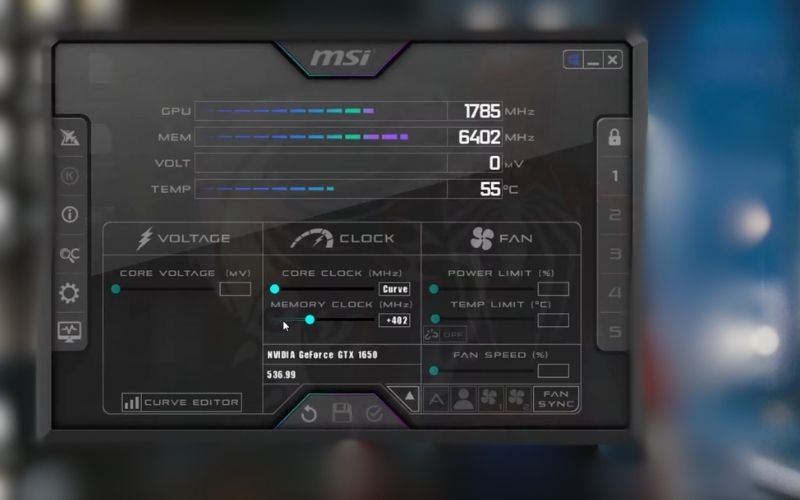
- GPU-Z: A lightweight information and monitoring tool that displays detailed specifications, temperature, and usage statistics.
Conclusion
Ensuring your GPU maintains a sustainable temperature is crucial for both optimal performance and longevity. By understanding the factors that impact GPU temperature, regularly monitoring its temperature, and proactively implementing safety measures, you can maintain a stable, high-performing system that endures over time.
Remember to strike a balance between performance and temperature to maximize your GPU’s lifespan